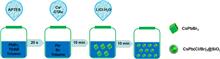
There are many strategies to maintain the excellent photoluminescence (PL) characteristics of perovskite quantum dots (QDs). Here, we proposed a facile and effective method to prepare cyan CsPb(Cl/Br)3/SiO2 nanospheres at room temperature. Cubic CsPb(Cl/Br)3 was obtained by adding a LiCl-H2O solution and anion exchange reaction. With (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane as an auxiliary agent, a QDs/SiO2 composite was extracted from a sol-gel solution by precipitate-encapsulation method. The transmission electron microscopy images and Fourier transform infrared spectra indicated the QDs were indeed embedded in silica substances. Besides, humidity stability and thermal stability show the composite possesses a great application value. Finally, cyan QDs@SiO2 powder has a high PL quantum yield of up to 84%; the stable cyan fluorescent powder does have great potential to play a key role in commercial full spectrum display.
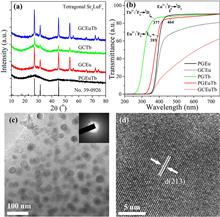
To introduce ordered nano-structures inside a transparent amorphous matrix with superior optical and mechanical properties bears scientific and technological importance, yet limited success has been achieved. Here, via simple melting-quenching and subsequent thermal activation, we report the successful preparation of transparent nano-structured glass-ceramics embedded in Sr2LuF7 nano-crystals (~26 nm), as evidenced by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and high resolution TEM. The successful incorporation of dopants into formed Sr2LuF7 nano-crystals with low phonon energy results in highly tunable blue–green photoemission, which depends on excitation wavelength, dopant type, and temperature. We found that Eu3+ and Eu2+ ions co-exist in this hybrid optical material, accompanied by the broadband blue emission of Eu2+ and sharp red emissions of Eu3+. A series of optical characterizations are summoned, including emission/excitation spectrum and decay curve measurement, to reveal the reduction mechanism of Eu3+ to Eu2+. Furthermore, near green–white photoemission is achieved via the enrichment of Tb3+/Eu3+ into crystallized Sr2LuF7 nano-crystals. The temperature-dependent visible photoemission reveals thermal activation energy increases with the precipitation of Sr2LuF7 nano-crystals in a glass matrix, suggesting better thermal stability of glass-ceramics than precursor glasses. These results could not only deepen the understanding of glass-ceramics but also indicate the promising potential of Eu3+/Tb3+-ions-doped Sr2LuF7 glass-ceramics for UV pumped white light emitting diodes (WLEDs) with good thermal stability.
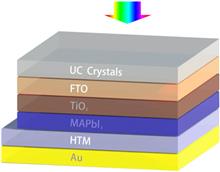
Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystals used as a spectral up-converter to improve the power conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells are prepared via an improved Bridgman approach. Green and red up-conversion (UC) emissions under the excitation of near-infrared (NIR) bands of 900–1000 nm and 1400–1600 nm can be observed. The effectiveness of the prepared materials as a spectral converter is verified by the enhancement of power conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells. The sample with a UC layer is 15.5% more efficient in converting sunlight to electricity compared to the UC layer-free sample due to the absorption of sunlight in the NIR range. The results suggest the synthesized Yb3+/Er3+ co-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystals are suitable for enhancing the performance of perovskite solar cells.
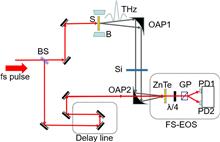
The ultrafast spin dynamic of in-plane magnetized Fe/Pt films was investigated by terahertz emission spectroscopy. The amplitude of the emitted terahertz wave is proportional to the intensity of the exciting laser beams. Both the amplitude and polarity of the terahertz wave can be adjusted by modifying the external magnetic field. The dependency of the amplitude on external magnetic fields is coincident to the hysteresis loops of the sample. Also, the polarity of the terahertz wave is reversed, as the magnetization orientation is reversed. The super-diffusive transient spin current with an inverse spin Hall effect is attributed to the main mechanism of the terahertz emission.
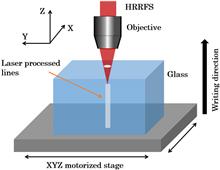
We report on the elemental redistribution behavior in oxyfluoride glasses with a high repetition rate near-infrared femtosecond laser. Elemental analysis by an electro-probe microanalyzer demonstrates that the redistributions of Ca2+ and Yb3+ ions change dramatically with pulse energy, which are quite different compared with previous reported results. Confocal fluorescence spectra of Yb3+ ions demonstrate that the luminescence intensity changes obviously with the elemental redistribution. The mechanism of the observed phenomenon is discussed. This observation may have potential applications in the fabrication of micro-optical devices.
The apatite compound Ca4La6(SiO4)4(PO4)2O2 (CLSPO) was explored as the host material for phosphors used in white light-emitting diodes (wLEDs). The crystal structure of the CLSPO host prepared by the solid-state reaction method was investigated with Rietveld refinement. The rare earth ions (Eu3+/ Tb3+/Ce3+, Tb3+/Tb3+, Mn2+) activated CLSPO phosphors were synthesized, and their photoluminescence properties, quantum yields, as well as thermal stabilities, were studied. Under near-ultraviolet excitations, the Eu3+ and Tb3+-doped CLSPO compounds exhibited red and green emissions with high luminescence efficiencies. Besides, tunable emissions from green to orange were obtained by introducing Mn2+ ions into the Tb3+-doped CLSPO samples. The results showed that the phosphors studied may have potential applications for wLEDs.
A time-resolved high-power laser photometer, which measures the real-time variations of transmission, internal reflection, and scattering simultaneously with picosecond time resolution, was developed to investigate the material response sequence during high-power nanosecond laser irradiation in thick fused silica. It was found that the transient transmission decreased sharply, accompanied by an increase in internal reflection at the rising edge of the laser pulse. The transient transmission recovered, while laser damage did not occur, but it did not recover if the scattering increased, indicating the occurrence of laser damage. The reason for the sharp decrease of transmission and the relationship between the transmission drop and laser damage were discussed.
This Letter presents a double-layer structure combining a cracked cross meta-surface and grating surface to realize arbitrary incident linear terahertz (THz) wave polarization conversion. The arbitrary incident linear polarization THz wave will be induced with the same resonant modes in the unit cell, which results in polarization conversion insensitive to the linear polarization angle. Moreover, the zigzag-shaped resonant surface current leads to a strong magnetic resonance between the meta-surface and gratings, which enhances the conversion efficiency. The experimental results show that a more than 70% conversion rate can be achieved under arbitrary linear polarization within a wide frequency band. Moreover, around 0.89 THz nearly perfect polarization conversion is realized.
Fractional density of states (FDOS) hinders the accurate measuring of the overall spontaneous emission (SE) control ability of a three-dimensional (3D) photonic crystal (PC) with the current widely used SE decay lifetime measurement systems. Based on analyzing the FDOS property of a 3D PC from theory and simulation, the excitation focal spot position averaged FDOS with a distribution broadening parameter was proposed to accurately reflect the overall SE control ability of the 3D PC. Experimental work was done to confirm that our proposal is effective, which can contribute to comprehensively characterizing the SE control performance of photonic devices with quantified parameters.
The photoelectric properties of In0.3Ga0.7As solar cells applied in laser wireless power transmission (LWPT) were studied when they were irradiated by 1070 nm continuous wave (CW) laser of various intensities. The influences of laser intensity on solar cell parameters extracted by the pollination algorithm were analyzed quantitatively. Results show that the conversion efficiency of the cell rose to the maximum and then decreased rapidly in the laser intensity range of 50–900 mW/cm2. With higher energy laser irradiation, the rise of ideality factor and reverse saturation current would lead to the degradation of voltage at the maximum power point, which was the main reason for the decrease of conversion efficiency. The results provide the basis for choosing the appropriate input energy in the case of different transmission systems.
The design of a conventional zoom lens is always challenging because it requires not only sophisticated optical design strategy, but also complex and precise mechanical structures for system adjustment. Here, we propose a continuous-zoom lens consisting of two chiral geometric metasurfaces with dielectric nanobrick arrays sitting on a transparent substrate. The metalens can continuously vary the focal length by rotating either of the two metasurfaces around its optical axis without changing any other conditions. Due to the polarization dependence of the geometric metasurface, the positive and negative polarities are interchangeable in one identical metalens only by changing the handedness of the incident circularly polarized light, which can generate varying focal lengths ranging from ∞ to +∞ in principle.
In this work, Er-doped aluminum nitride (AlN), Pr-doped AlN, and Er, Pr co-doped AlN thin films were prepared by ion implantation. After annealing, the luminescence properties were investigated by cathodoluminescence. Some new and interesting phenomena were observed. The peak at 480 nm was observed only for Er-doped AlN. However, for Er, Pr co-doped AlN, it disappeared. At the same time, a new peak at 494 nm was observed, although it was not observed for Er-doped AlN or Pr-doped AlN before. Therefore, the energy transfer mechanism between Er3+ and Pr3+ in AlN thin films was investigated in detail. Through optimizing the dose ratio of Er3+ with respect to Pr3+, white light emission with an International Commission on Illumination chromaticity coordinate (0.332, 0.332) was obtained. This work may provide a new strategy for realizing white light emission based on nitride semiconductors.
Ho3+/Yb3+: BaMoO4 phosphors with different concentrations were fabricated by a gel combustion method. The upconversion (UC) luminescence, intrinsic optical bistability, and the corresponding mechanisms were reported for the present system. The optical thermometric properties based on red (5F5→5I8) and green (5F4/5S2→5I8) emissions were studied. The sensing sensitivities could be tuned by manipulating the cooperative energy transfer process. The highest absolute sensitivity was 99 × 10 4 K 1 at 573 K, which is larger than that of many previous UC materials.
Phosphor in glass (PiG) employing Ce:Y3Al5O12 (YAG)-doped boro-bismuthate glass via low-temperature co-sintering technology was successfully prepared, using Bi2O3-B2O3-ZnO glass as the base material. The photoluminescence (PL) of PiG co-sintered at times ranging from 20 min to 60 min at 700°C was investigated. As a result, the relative PL intensity of PiG under a reducing atmosphere of CO showed significant enhancement of about 7–14 times that under air atmosphere sintering for 20–50 min. The PL intensity decreased gradually with the co-sintering time, which may be due to the corrosion of the YAG lattice structure.
In this Letter, we demonstrate a linear polarization conversion of transmitted terahertz wave with double-layer meta-grating surfaces, which integrated the frequency selectivity of a split ring resonator metasurface and the polarization selectivity of a metallic grating surface. Since the double-layer can reduce the loss, and the Fabry–Perot like resonant effect between the two layers can improve the conversion efficiency, this converter can rotate the incident y-polarized terahertz wave into an x-polarized transmitted wave with relatively low loss and high efficiency. Experimental results show that an average conversion efficiency exceeding 75% from 0.25 to 0.65 THz with the highest efficiency of 90% at 0.43 THz with only 2 dB loss has been achieved.
We studied Goos–H nchen (GH) shifts on a reflective phase-gradient-produced metasurface. Their analytical solutions were achieved for both TE and TM polarizations utilizing the generalized Snell’s law. The calculated results show that the GH shifts are evidently affected by phase gradients and incident angles, which means that a certain range of GH shifts can be realized as long as an incident angle, phase gradient, and frequency are properly chosen. This offers an effective method for the control of GH shifts.
A 0.1 mol.% CoF2-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystal with high quality in the size of ~ 10 mm×100 mm was grown by the Bridgman method. Three peaks located at 504, 544, and 688 nm and a broad band in the range of 1200–1600 nm centered at 1472 nm were observed in the absorption spectra. The absorption peak position suggests cobalt ions in the divalent state in the grown crystal. Moreover, the cobalt ions are confirmed to locate in the distorted cubic crystal structure. Upon excitation of 500 nm light, a sharp emission peak at 747 nm ascribed to the T22(H1)→4A2(F) transition was observed for the crystal. The Co2+-doped Na5Lu9F32 crystal shows a potentially promising material for the application of a passively Q-switched laser operating in the near-infrared range.
Laser-induced modification at 355 nm of deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (DKDP) crystals following exposure to nanosecond (ns) and sub-ns laser irradiation is investigated in order to probe the absorption mechanism in damage initiation. Laser damage resistance is greatly improved by sub-ns laser conditioning, whereas only a little improvement occurred after ns laser conditioning at the same laser fluence. Moreover, scattering and transmittance variations after the two types of laser conditioning indicate similar reduction of linear absorption. However, by contrast, large differences on nonlinear absorption modification are discovered using Z-scan measurement. This characteristic absorption modification by laser irradiation provides evidence that a nonlinear absorption mechanism plays a key role in damage initiation at 355 nm.
A series of Ce3+, Sm3+-doped Zn2GeO4 phosphors are prepared by the solid-state reaction. A blue photoluminescence (PL) of Zn2GeO4 is observed as the recombination of the electrons trapped on VO and Zni with holes trapped on VGe and VZn′. The energy transfer process between Ce3+ and Sm3+ is confirmed by the PL spectra and decay curves, and the emission colors can be adjusted from blue to orange–red. Furthermore, we verify unambiguously that the energy transfer from Ce3+ to Sm3+ occurs. Besides, Ce3+</inline-
The polarization state of transmitted light is linked to liquid crystal (LC) molecular distribution. The dynamic behavior of a twisted nematic LC molecule is measured with a home-built 10 kHz snapshot polarimeter. Only the transient molecule rotations are observed when the external voltage changes, and the molecules return to their original orientations quickly even when high voltage is applied. Our observations cannot be attributed to the traditional electro-optic effect. The invalidation of the static external field indicates the shielding effect of redistributing impurity ions in an LC cell.
In this work, we investigate a new type of fluoride glasses modified by Al(PO3)3 with various Tm3+/Ho3+ doping concentrations. The introduced PO3 plays an effective role in improving the glass-forming ability and thermal stability. Besides, 1.47, 1.8, and 2.0 μm emissions originating from Tm3+ and Ho3+, respectively, are observed. The spectroscopic properties and energy transfer mechanisms between Tm3+ and Ho3+ are analyzed as well. It is noted that the higher predicted spontaneous transition probability (118.74 s 1) along with the larger product of measured decay lifetime and the emission cross section (σemi×τ) give evidence of intense 2.0 μm fluorescence.
The plasmonic mode in graphene metamaterial provides a new approach to manipulate terahertz (THz) waves. Graphene-based split ring resonator (SRR) metamaterial is proposed with the capacity for modulating transmitted THz waves under normal and oblique incidence. Here, we theoretically demonstrate that the resonant strength of the dipolar mode can be significantly enhanced by enlarging the arm-width of the SRR and by stacking graphene layers. The principal mechanism of light–matter interaction in graphene metamaterial provides a dynamical modulation based on the controllable graphene Fermi level. This graphene-based design paves the way for a myriad of important THz applications, such as optical modulators, absorbers, polarizers, etc.
In order to realize single emissive white phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices (PHOLEDs) with three color phosphorescent dopants (red, green, and blue), the energy transfer between the host material and the three dopants, as well as the among the three dopants themselves, should be considered and optimized. To explore the effect of red phosphorescent dopant on the color rendering index (CRI), the authors investigate the wavelength position of the maximum emission peak from three phosphorescent dopants. The CRI and luminous efficiency of white PHOLED in which Ir(pq)2(acac) acts as the red phosphorescent dopant are found to be greater than those of devices prepared using Ir(piq)3 and Ir(btp)2(acac) as the emission spectrum has a relatively high intensity near the human perception of blue, red, and green wavelengths. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the performance of the three dopants is related to the absorption characteristics of the red phosphorescent dopant. With a maximum emission peak at 600 nm, Ir(pq)2(acac) has a higher intensity in the concave section between 550 and 600 nm seen for red and blue dopants. In addition, the long metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) absorption tail of Ir(pq)2(acac) overlaps with the emission spectra of the green dopant, enhancing emission. Such energy transfer mechanisms are confirmed to optimize white emission in the single emissive white PHOLEDs.
In this Letter, ceramic Nd:YAG is charactrizeby electron spin resonance (ESR) measurements. The ESR results indicate that the polycrystalline ceramic Nd:YAG has barely native defects and impurity ions localization defects, compared to an Nd:YAG crystal with the same Nd doping concentration, due to its density structure by sintering in a vacuum pure raw material and additives during the fabrication. It may conclude that the high quality ceramic Nd:YAG may have greater ability on optical characteristic, mechanical performance, and laser damage than that of the crystals, which is a promising candidate to use on laser diode-pumped solid-state lasers.
A series of RE3+ (RE=Eu/Tb/Ce)-activated Sr4La(PO4)3O (SLPO) phosphors are synthesized with a high-temperature solid-state reaction method. The photoluminescence properties, thermal stability, morphology, and CIE values of the SLPO:Eu3+/Tb3+/Ce3+ phosphors are investigated. Under 394 nm excitation, the SLPO:Eu3+ exhibits red emission, and the SLPO:Tb3+ presents a green emission upon 379 nm excitation, while Ce3+-doped SLPO has a broad emission band ranging from 370 to 650 nm under 337 nm excitation. The investigation results indicate that the SLPO:Eu3+/Tb3+/Ce3+ phosphors can be effectively excited by near-ultraviolet light and may have the potential to serve as red-, green-, and blue-emitting phosphors for applications in white light-emitting diodes.
Bismuth (Bi)-doped laser glasses and fiber devices have aroused wide attentions due to their unique potential to work in the new spectral range of 1 to 1.8 μm traditional laser ions, such as rare earth, cannot reach. Current Bi-doped silica glass fibers have to be made by modified chemical vapor deposition at a temperature higher than 2000°C. This unavoidably leads to the tremendous loss of Bi by evaporation, since the temperature is several hundred degrees Celsius higher than the Bi boiling temperature, and, therefore, trace Bi (~50 ppm) resides within the final product of silica fiber. So, the gain of such fiber is usually extremely low. One of the solutions is to make the fibers at a temperature much lower than the boiling temperature of Bi. The challenge for this is to find a lower melting point glass, which can stabilize Bi in the near infrared emission center and, meanwhile, does not lose glass transparency during fiber fabrication. None of previously reported Bi-doped multicomponent glasses can meet the prerequisite. Here, we, after hundreds of trials on optimization over glass components, activator content, melting temperature, etc., find a novel Bi-doped gallogermanate glass, which shows good tolerance to thermal impact and can accommodate a higher content of Bi. Consequently, we successfully manufacture the germanate fiber by a rod-in-tube technique at 850°C. The fiber exhibits similar luminescence to the bulk glass, and it shows saturated absorption at 808 nm rather than 980 nm as the incident power becomes higher than 4 W. Amplified spontaneous emissions are observed upon the pumps of either 980 or 1064 nm from germanate fiber.
The optical constants, photoluminescence properties, and resistivity of Al-Alq3 thin films prepared by the thermal co-evaporation method on a silicon substrate are studied with various Al fractions. A variable angle spectroscopic ellipsometry is employed to determine the optical constants in the wavelength from 300 to 1200 nm at incidence angles of 65°, 70°, and 75°, respectively. Both the refractive indices and extinction coefficient apparently increase with increasing Al fractions. The intensity of photoluminescence spectra gradually increases with decreasing Al fractions due to intrinsic energy level transition of Alq3 organic semiconductor in the ultraviolet wave band. The resistivity decreases from 42.1 to 3.36 Ω·cm with increasing Al fraction from 40% to 70%, resulting in a larger emission intensity in photoluminescence spectra for the 40% Al fraction sample.
A novel H-plane cross-shaped circulator based on magneto-photonic crystals is experimentally investigated. The band gap of the TE mode for the photonic crystals is calculated by the plane wave expansion method. The transmission characteristics of the circulator are simulated by the finite element method. We perform the experiments in the microwave regime to validate the numerical results. At the central frequency of 10.15 GHz, the measured isolation and insertion loss of the circulator reaches 30.2 and 3.93 dB, respectively. The bandwidth of the circulator is about 550 MHz. The optimal experimental value of isolation is higher than the numerical value.
We provide the first demonstration of pure red emission in the visible light region via three-photon excitation in monodisperse Na3ZrF7:Er nanoparticles (NPs) by using a laser operating in the telecommunication band. NPs of ~22 nm in diameter are synthesized at 260°C by the thermal decomposition method. The experimental results reveal that the Na3ZrF7:Er NPs exhibit pure red emission in the visible region under 1480 nm laser excitation, and the emission intensity is significantly influenced by the Er3+ ion concentration. The decay times of the S3/24→F415/2 and F9/24→F415/2 transitions of the Er3+ ions at 540 and 655 nm, respectively, are reduced by increasing the Er3+ ion concentration in the <mml:math display="inline" id="m9" xmlns:mml="http://ww
A highly Tm-doped lead germanate glass fiber is developed using the rod-in-tube method. The ~2 μm laser beam quality of the fiber is ~1.5. The lead germanate composite fiber jumpers are homemade for all the fiber laser investigations. When core is pumped by a 1590 nm Yb/Er fiber laser, a maximum laser output of 313 mW is achieved at a 670 mW pump power, and the corresponding slope efficiency is ~52.8%. Moreover, by using a 2 cm-long lead germanate fiber as the gain medium, a 33 mW 1942 nm Tm laser is also demonstrated.
Tb3+ and Sn2+ co-doped strontium phosphate glasses are prepared and their unique photoluminescence (PL) properties for deep UV excitation are investigated. With the co-doped Sn2+ ions, Tb3+ keeps the original PL behaviors under near UV excitation while its PL action for deep UV excitation is enhanced tremendously. PL emission and excitation spectra demonstrate the sensitization role of Sn2+ on the Tb3+ emissions for deep UV excitation that is associated with the strong deep UV absorption of Sn2+ for greatly enhancing the resonance of the Tb3+ excitation with the deep UV light source. The decay curves of Sn2+ and Tb3+ emissions for both singly doped and co-doped samples are single exponentially well fitted with almost the same emission lifetime (τ) values in the microsecond and millisecond time regimes, respectively, confirming that Sn2+ and Tb3+ act as an independent activator in the present phosphate glass matrix while an involved energy
We report on a novel dibenzothiophene-based two-photon fluorescent probe for selective nuclear bioimaging, which contains bilaterally symmetrical pyridine rings connected by a central conjugated-bridge dibenzothiophene. This probe possesses a large two-photon absorption cross-section of 471 GM, yields a 25-fold enhancement of the fluorescence titration, and a stronger photostability for nuclei labeling than existing probes. The real-time observation period is a minimum of 1800 s under a femtosecond laser excitation, which is significantly longer than that of 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. The above results confirm that this novel molecule is a suitable two-photon fluorescent probe for application to nuclear bioimaging in cells.
Cavity-coupled plasmonic structure is demonstrated to be a simple and effective tool to manipulatelight, enhance the biosensing figure of merit, and control the polarization state. In this Letter, we demonstrate the tunability of the chiroptical effect of cavity-coupled chiral structure, i.e., sandwich chiral metamaterials (SCMs), in whichradiation coupling dominates the interaction between particles. Two types of SCMs whose building blocks are 3D chiral and 2D chiral, respectively, are numerically studied. Distinct responses are observed in these two materials. The chiroptical effect can be effectively manipulated and enhanced in the 2D case, while the SCMs consisting of 3D chiral layers keep the chiroptical effecta constant. A theoretical analysis based on matrix optics is developed to explain the corresponding phenomena, which gives a reasonable agreement with numerical simulations.
A Ce3+ ion-doped α-NaYF4 single crystal of high quality is grown successfully by an improved flux Bridgman method under the conditions of taking the chemical raw composition of NaF:KF:YF3:CeF3 in the molar ratio of 30∶18∶48∶4, where the KF is shown to be an effective assistant flux. The x ray diffraction, absorption spectra, excitation spectra, and emission spectra of the Ce3+-doped α-NaYF4 single crystal are measured to investigate the phase and optical properties of the single crystals. The absorption spectrum of the Ce3+:α-NaYF4 shows a strong band that peaks at the wavelength of 300 nm. The emission spectrum of the Ce3+:α-NaYF4 emits an intense ultraviolet (UV) band at the wavelength of 332 nm under the excitation of 300 nm light. Two separated luminous bands of 330 and 350 nm, which correspond to the transitions 5d→F5/22 and 5<
Silicon-rich oxide films with controllable optical constants and properties are deposited by the reactive magnetron sputtering method on a Si target. The O/Si atomic ratio x of SiOx is tuned from 0.12 to 1.84 by adjusting the oxygen flow rate, which is found to be a more effective way to obtain SiOx films compared with changing the oxygen content [O2/(Ar+O2) ratio]. The optical properties of SiOx films can be tuned from semiconductor to dielectric as a function of ratio x. The structures and components are also investigated by an x ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of the Si 2p core levels, the results of which exhibit that the structures of SiOx can be thoroughly described by the random bonding model.
Er ions are implanted into the GaN thick films grown by hydride vapor phase epitaxy. The implantation energy is 200 keV and the implantation doses are 1×1013, 1×1014, 1×1015, and 5×1015 atom/cm2, respectively. The effects of the implantation dose and annealing temperature on the GaN band-edge luminescence are investigated. The cathodoluminescence spectra from 82 to 323 K are measured for 1×1015 atom/cm2-implanted GaN annealed at 1100°C. Luminescence peaks at 356, 362, 376, 390, and 414 nm are observed on the 82 K cathodoluminescence spectrum. When the temperature is increased to 150 K, the intensities of the 356 and 414 nm peaks are nearly unchanged and the 362, 376, and 390 nm peaks disappear. The intensity ratio of 538 nm (H11/22→I15/24) and 559 nm (S3/24→I15/24) is increased with the increase in temperature. We try to shed light on the above interesting phen
This Letter is concerned with the influence of polarization on the damage performance of type I doubler potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals grown by the conventional growth method under 532 nm pulse irradiation. Pinpoint density (ppd) and the size distribution of pinpoints are extracted through light scattering pictures captured by microscope. The results show that the ppd of polarization that parallels the extraordinary axis is around 1.5× less than that of polarization that parallels the ordinary axis under the same fluence, although polarization has no influence on size distribution of pinpoints. We also find that the size distribution is independent of fluence, although the number of pinpoints grows with fluence.
The fluorescence of graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) that are infiltrated into porous silicon (PSi) is investigated. By dropping activated GOQDs solution onto silanized PSi samples, GOQDs are successfully infiltrated into a PSi device. The results indicate that the intensity of the fluorescence of the GOQD-infiltrated multilayer with a high reflection band located at its fluorescence spectra scope is approximately double that of the single layer sample. This indicates that the multilayer GOQD-infiltrated PSi substrate is a suitable material for the preparation of sensitive photoluminescence biosensors.
A highly transparent Eu3+-doped CaGdAlO4 (CGA) single crystal is grown by the floating zone method. The segregation coefficient, x ray diffraction, and x ray rocking curve are detected, and the results reveal that the single crystal is of high quality. The f–f transitions of Eu3+ in the host lattice are discussed. The D05–F72 emission transition at 621 nm (red light) is dominant over the D05–F71 emission transitions at 591 and 599 nm (orange light), agreeing well with the random crystal environment of Eu3+ ions in a CGA crystal. The decay time of Eu:D05 is measured to be 1.02 ms. All the results show that the Eu:CGA crystal has good optical characterization and promises to be an excellent red- fluorescence material.
The use of red light or near-infrared radiation as a luminescent probe for in vivo bio imaging is crucial in order to restrict the strong absorption of short-wavelength light below 600 nm in tissue. It is demonstrated that the emission color of Yb/Ho codoped NaYF4 nanoparticles can be tuned from green to red by incorporating Ce3+ ions. However, compared with that of the NaYF4:Yb/Ho nanoparticles, the photoluminescence intensity of the Ce3+-tridoped NaYF4:Yb/Ho nanoparticles is drastically reduced. In this work, Ce3+-incorporated core/shell NaYF4:Yb3+50%@NaYF4:Ho3+0.5% nanoparticles are prepared. A strong red emission and a high-intensity ratio between the red emission and green emission are obtained in these upconversion nanoparticles. The emission intensity increases by a factor higher than 120 when compared with that of the NaYF4:Yb/Ho/Ce nanoparticles. This result indicates that the Ce3+ incorporation into the <mml:math display="inline" id="m11" xmlns:mml="http://www.w
This Letter presents the fabrication and characterization of a perylene (Per) and Rhodamine 6 G (Rh 6 G) co-doped polymeric fiber. The spectroscopic properties (luminescence spectra, attenuation, energy transfer) of the co-doped polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) fiber are presented. Two different concentrations of Rh 6 G (2.2×10 4 and 4.1×10 4 mol/L) and a constant Per concentration (6.2×10 4 mol/L) are used in the experiments. The luminescence spectrum changes versus the fiber length are discussed. Additionally, the ratio of the maximum fluorescence peaks of the used dyes is calculated versus the fiber length. The obtained results show the energy transfer from Per (donor) to Rh 6 G (acceptor). The proposed co-doped fiber can be used in applications in lighting and sensor technology.
This Letter presents an original technique to design and synthesize an inhomogeneous asymmetrical lens resulting in a special fan-beam radiation pattern in a wide frequency bandwidth. The vertical and horizontal planes of the fan-beam radiation pattern can be determined separately. Wide angle search and detection are achievable by using this type of lens antenna because of its suitable radiation pattern. The proposed relative index profile is validated by the means of commercial CST software and an FDTD scheme.
Wavelength-dependent birefringence and dielectric anisotropy, two major optical properties of the nematic liquid crystal materials used in phase-only liquid crystal on silicon (LCOS) devices, are measured as a function of operating temperatures. The dynamic phase modulation depth and threshold voltage of these phase-only LCOS devices are also measured in the corresponding temperature range and compared with theoretical predictions. The results show that the dynamic response time can be reduced significantly by an appropriate increase of device operative temperature, while the necessary device elements, such as phase modulation depth and threshold voltage, can be maintained at the same time.
The interference of optically induced electric and magnetic resonances in high-refractive-index dielectric nanoparticles provides a new approach to control and shape the scattering patterns of light in the field of nanophotonics. In this Letter, we spectrally tune the electric and magnetic resonances by varying the geometry of a single isolated lead telluride (PbTe) dielectric nanocube. Then, we overlap the electric dipole resonance and magnetic dipole resonance to suppress backward scattering and enhance forward scattering in the resonance region. Furthermore, a broadband unidirectional scattering is achieved by structuring the dielectric nanocuboids as a trimer antenna.
To investigate the relationship between indium content and optical properties during epitaxial growth of an InGaAs/GaAs single quantum well (SQW), simulation and experiments are demonstrated. The epitaxial growth is demonstrated with low-pressure metal–organic chemical vapor deposition. Photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy is applied to research the PL properties at room temperature. The In/(In+Ga) varies from 0.24 to 0.36, resulting in an increasing of the full-width half-maximum (FWHM) with the wavelength exhibiting a red-shift. A SQW with an In/(In+Ga) of 0.36 is manufactured, where a FWHM of 23.9 meV is obtained. An InGaAs SQW sandwiched by GaAsP is prepared, which is observed to exhibit a diminished FWHM of 17.0 meV with the wavelength revealing a blue-shift.
We investigate the one/two-photon fluorescence of two synthesized phenoxy-phthalocyanines (Pc1 and Pc2) using the mild reaction coordination method and the nonlinear optical properties of Pc1 and Pc2 in solution are investigated using the Z-scan technique at 800 with a 100 fs pulse width. The results show that both phthalocyanines indicate strong three-photon absorption, and the critical intensity value of Pc2 is higher than that of Pc1 when the contribution of the high excited-state absorption is introduced in the sample. Furthermore, the redshift of one- and two-photon fluorescence spectra can be explained by the reabsorption effect of the molecules. With good solubility and excellent nonlinear optical properties, the samples are expected to be a potential candidate for optical applications and photodynamic therapy.
We theoretically study the optimum design of anisotropic acousto-optic modulator (AOM) based on lithium niobate crystal. Four different kinds of operating modes in the XOZ and YOZ acousto-optic (AO) planes are systematically analyzed by the tangent condition theory and the optimized operating mode is determined. Furthermore, the dependence of the AO merit on the operating frequency and the off-axis angle of the AOM are also obtained by numerical simulations.
Glass ceramics Ba2LaF7:xDy3+ are obtained through the conventional melt-quenching technique, and their luminescent properties are investigated. Under 350 nm excitation, the emission spectra consists of a strong blue-yellow band as well as a weak red emission centered at 660 nm, which are attributed to the F9/24→H15/26, F9/24→H13/26 and F9/24→H11/26 transitions of the Dy3+ ion, respectively. The corresponding Commission Internationale de L’Eclairage (CIE) chromaticity coordinate for a sample of 2 mol.% Dy2O3 after being heat-treated at 690°C is (0.313, 0.328). It is concluded that the formed materials may have the possibility of applications for white light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
A geometry of transient-grating self-referenced spectral interferometry (TG-SRSI) is proposed for weak femtosecond pulse characterization. By using a reflective microscope objective (RMO), we build a compact, robust, and easy to adjust device with a higher sensitivity to pulse energy in comparison to all previous SRSI methods. A 65 nJ/~40 fs/1 kHz pulse at 800 nm is successfully characterized, which speaks to the capability of our device to characterize a weak pulse. It is expected to extend the TG-SRSI method to the characterization of femtosecond pulses from oscillators in the near future.
We demonstrate a soft lithography approach for fabrication of a topographically patterned polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) liquid-crystal (LC) alignment layer. This specific approach employs modified micromolding in capillaries for negative replication of the PVA microstructures on indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates from patterned poly(dimethylsiloxane) molds in a single step, leading to planar alignment on the desired regions. By doping with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanoparticles, which can induce vertical alignment on bare ITO surfaces, periodic LC phase gratings based on an alternating vertical-aligned/hybrid-aligned nematic geometry are presented as an application, and a theoretical model was used to simulate and examine the experimental results.
We report an Er3+-doped fluorogallate glass with good thermal and chemical stability. The low maximum phonon energy and high mid-infrared (IR) transmittance of the glass are confirmed by Raman and IR spectra, respectively. Based on Judd–Ofelt theory, intensity parameters and radiative properties are determined from the absorption and emission spectra. The proposed glass possesses a large fluorescence branching ratio β (21.71%) and a maximum stimulated emission cross-section σem of Er3+:I11/24→I13/24 transition at 2.71 μm (1.04×10 20 cm2). The results indicate that it can be potentially applied in high-power 2.7 μm fiber lasers.
The inclusions in conventionally grown KD2PO4 (DKDP) crystals are investigated. The inclusions are captured by a light-scattering technique. The sizes are determined by an optical microscope and a transmission electron microscope (TEM), and the compositions are analyzed by time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) and an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). Two kinds of inclusions are observed in the DKDP crystals: a submicron-scale inclusion and a micron-scale inclusion. The typical submicron-scale inclusions contain growth solution, and their sizes range from tens to hundreds of nanometers, whereas the micron-scale inclusions contain growth solution and the metal element Na, and the sizes are tens of microns. The possible formation mechanisms of the inclusions are discussed, and the influence of the inclusions on laser-induced damage behaviors are analyzed and discussed.
The absorption spectra, excitation spectra, and emission spectra of Tb3+/Eu3+ ions in LiYF4 single crystals synthesized by an improved Bridgman method are measured. The emission spectra of several bands, mainly located at blue ~487 nm (Tb:D45→F76), yellowish green ~542 nm (Tb:D45→F75), and red ~611 nm (Eu:D05→F72) wavelengths, are observed under excitation by UV light. An ideal white light emission as a result of simultaneous combination of these emissions can be obtained from 1.11 mol% <mml:math display=
Pr3+/Yb3+ co-doped CaNb2O6 thin films are deposited on Si(100) substrates by pulsed laser deposition and annealed at different temperatures in air atmosphere. X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and photoluminescence spectra are used to characterize the samples. The results show that the annealing temperature has a strong effect on the film’s grain size, structure, morphology, and the up-conversion luminescence properties. The grain size and up-conversion luminescence of Pr3+/Yb3+ co-doped CaNb2O6 films increases with the increasing annealing temperature.
In this work, the absorption, fluorescence spectra, and fluorescence decay curve of Nd:Lu3Al5O12, i.e., neodymium lutetium aluminum garnet (Nd:LuAG) ceramic are investigated. A diode-end-pumped Nd:LuAG ceramic laser is demonstrated for the first time (to our knowledge). We present the experiment results of Nd:LuAG ceramic’s continuous wave (CW) and electro-optically (E-O) Q-switched performance. CW output power of 2.5 W is obtained, corresponding to optical-to-optical efficiency of 17.2% and slope efficiency of 24.3%. For the E-O Q-switched setup, the shortest pulse width and the largest pulse energy are measured to be 4.8 ns and 1.96 mJ, respectively. Its optical-to-optical efficiency and the slope efficiency are 17.3% and 28.7%, respectively.
We present a tunable resonator consisting of a colossal magnetoresistant cross in which a smaller gold cross is embedded. Simulations show the resonance frequencies of the resonator move into the infrared regime when there is a change in the intensity of the external magnetic field applied to the resonator. The source of the tunability is the variance in the colossal magnetoresistance in the resonator when the intensity of the magnetic field changes, which accordingly leads to a shift in the resonance frequency. Such a method offers a new way to achieve tunability, which has potential applications in controllable photoelectric elements.
Refractive indices for crystals ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), 30% deuterated ADP (DADP), 50% DADP, and 70% DADP are measured from 253 to 1529 nm with 5×10 6 accuracy. Numerical fits to modified double-pole Sellmeier equation are made. Second-harmonic generation, third-harmonic generation phase matching (PM) angles, and noncritical PM (NCPM) wavelengths are calculated using the Sellmeier parameters. The deuterated crystals show smaller PM angles than pure crystal. Fourth-harmonic generation process can be realized by DADP in smaller deuterium content than deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (DKDP). The measured NCPM wavelengths are consistent with the calculated value. PM characteristics are compared between DADP and DKDP.
Tb3Ga5O12 (TGG) is an excellent material for magneto-optical applications, and is the key component in Faraday isolators (FIs). The preparation process of transparent TGG ceramics is experimentally studied. The optical quality and the microstructure of the samples are investigated. The results show that the transmittance of the sample sintered at 1550°C is close to 72% in the region of 500–1500 nm. The Verdet constant at 632.8 nm measured at room temperature is 125.01 rad T 1 m 1, which is almost the same as that of a single crystal.
Tb3Ga5O12 (TGG) is an excellent material for magneto-optical applications, and is the key component in Faraday isolators (FIs). The preparation process of transparent TGG ceramics is experimentally studied. The optical quality and the microstructure of the samples are investigated. The results show that the transmittance of the sample sintered at 1550°C is close to 72% in the region of 500–1500 nm. The Verdet constant at 632.8 nm measured at room temperature is 125.01 rad T 1 m 1, which is almost the same as that of a single crystal.
Li+-doped HoPO4 powders with a pure tetragonal phase are successfully synthesized by the co-precipitation method. It exhibits an obvious color change under sunlight and tri-phosphor fluorescent light illumination. The introduction of Li+ ions into HoPO4 can further enhance its photochromic property effectively. The doped Li+ ions induce changes in the crystal structure. The spectral characteristics and thus photochromic properties of HoPO4 are explored. The improved HoPO4 powder, when used as a photochromic material, has wide-ranging prospects in security, decoration, and other applications.
Infrared-to-visible upconverted luminescent spectra of Er3+ and La3+ codoped Y2O3 powders are investigated. By introducing La3+ ions, the upconversion green radiation is found to be greatly enhanced when compared with the powders with La3+ absent. Such enhancement can be attributed to the modification of the local symmetry surrounding the Er3+ ion, which benefits the intra-4f transitions of Er3+ ion, and the decreasing interaction between Er3+ ions, which suppresses the energy transfer process F7/24+I411/2→F49/2+F49/2</mml
The films of few-layer graphene are formed through laser exfoliation of a highly ordered pyrolytic graphite (HOPG), without a catalytic layer for the growth process. The femtosecond (fs) laser exfoliation process is investigated at different laser fluences and substrate temperature. For fs laser exfoliation of HOPG, the few-layer graphene is obtained at 473 K under an optimal laser fluence. The formation of few-layer graphene is explained by removal of intact graphite sheets occurred by an optimal laser fluence ablation. The new insights may facilitate the controllable synthesis of large area few-layer graphene.
Research on light scattering from a large chiral sphere shows that the rainbow phenomenon is different from that of an isotropic sphere. A chiral sphere with certain chirality generates three first-order rainbows. In this Letter, we present a geometric optics interpretation for the phenomenon and make a calculation of the rainbow angles. The ray traces inside the sphere are determined by the reflection and refraction laws of light at the achiral–chiral interface and the chiral–achiral interface. The calculated rainbow angles achieve good agreements with those obtained by the analytical solutions. The effects of chirality and the refractive index of the sphere on rainbow angles are analyzed.
In this Letter, new concepts of fluorescence phase-change materials and fluorescence phase-change multilevel recording are proposed. High-contrast fluorescence between the amorphous and crystalline states is achieved in nickel- or bismuth-doped Ge2Sb2Te5 phase-change memory thin films. Opposite phase-selective fluorescence effects are observed when different doping ions are used. The fluorescence intensity is sensitive to the crystallization degree of the films. This characteristic can be applied in reconfigurable multi-state memory and other logic devices. It also has likely applications in display and data visualization.
Zinc strontium phosphate glasses doped with different trivalent praseodymium ion (Pr3+) concentrations are presented and their photoluminescence properties are investigated upon 442 nm excitation. With the Pr3+ concentration decreasing, the orange emission of Pr3+ (D21 HJ3) is enhanced steadily at the cost of its blue emission (P1,03 H43). Monochromic orange emission of Pr3+ ions is obtained when the Pr3+ doping is reduced to 0.05 mol.%. The mechanism controlling the monochromatic characteristic of Pr3+ emissions is supposed to be associated with the phonon-aided nonradiative relaxation process of Pr3+: Pj3→</mml:mo
A polarization-insensitive, square split-ring resonator (SSRR) is simulated and experimented. By investigating the influence of the asymmetrical arm width in typical SSRRs, we find that the variation of the arm width enables a blue shift of the resonance frequency for the 0° polarized wave and a red shift of the resonance frequency for the 90° polarized wave. Thus, the resonance frequency for the 0° polarized wave and the resonance frequency for the 90° polarized wave will be identical by asymmetrically adjusting the arm width of the SSRR. Two modified, split-ring resonators (MSRRs) that are insensitive to the polarization with asymmetrical arm widths are designed, fabricated, and tested. Excellent agreement between the simulations and experiments for the MSRRs demonstrates the polarization insensitivity with asymmetrical arm widths. This work opens new opportunities for the investigation of polarization-insensitive, split-ring resonator metamaterials and will broaden the applications of split-ring resonators in various terahertz devices.
We present theoretical studies on the wideband design of bulk lithium niobate (LN) acousto-optic deflector (AOD) through the walk-off design of the ultrasonic vector, which satisfies the momentum match condition. The ultrasonic properties of LN crystal are studied by solving the Christopher equation and the reciprocal velocity curves in the operating planes XOZ and YOZ are systematically obtained. The calculation results show that the bandwidth of the AOD is highly dependent on the incident angle of light beam and the velocity of the ultrasonic waves, which show strict linear properties in the operating bandwidth. Furthermore, the dependence of the central frequency of the AOD on the angle of incident light and the ultrasonic velocity are also analyzed.
Re3+, Yb3+ co-doped (Re0.005YbxY(0.995-x))3Al5O12 [Re = Ce, Er, x = 0, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2] transparent ceramics are synthesized by the solid state reaction and vacuum sintering as the down-conversion (DC) materials. The photoluminescence excitation and the photoluminescence spectra demonstrate the near-infrared quantum cutting (QC) and the energy transfer (ET) from Re3+ to Yb3+ in both of these series of samples. The comparison of the near-infrared QC spectra of the two series of samples shows that the Ce3+, Yb3+ co-doped Y3Al5O12 transparent ceramic samples have much higher intensity of the emission spectra in the near-infrared region, and higher ET efficiency than the Er3+, Yb3+ co-doped ones. So, the Ce3+, Yb3+ DC ion pair is a better choice to improve the efficiency of the crystalline silicon-based solar cells.
In this study, based on magnetic tunable characteristics of nanoparticle magnetic fluid, we design the photonic crystals' defect-localized modes with a defect layer of nanoparticle magnetic fluids. The transmission spectrum of one-dimensional photonic crystals with a defect layer of nanoparticle magnetic fluid is calculated numerically using the transfer matrix method. The results indicate that the wavelength of defect localized modes moves to short wave with the increasing of magnetic field intensity. The maximum variation is 7 nm. When the thickness deviation of defect layer is in the range of 5 nm, the variation of the wavelength is 6 nm. The bandwidth of the defect localized modes is 0.2 nm and its quality factor is of the order of 103. Therefore, the variation of the wavelength of defect-localized modes, which is caused by the thickness deviation of a defect layer, could be compensated by changing the magnetic field. In this study, the defect-localized modes with a certain wavelength are realized.
A planar-hyperlens-based imaging device is presented in this paper. Based on the structure of hyperbolic dispersion metamaterial and with the ability of collecting the evanescent waves from the object, the planar hyperlens can deliver and magnify the super-resolution details of a planar object to the extent that a traditional microscopic objective can resolve them. The super-resolution magnification imaging principle of the device was analyzed, and the relations of the imaging resolution and magnification with the structure parameters of the device were deduced. With careful design, the effectiveness of the device was confirmed in a series of numerical simulations.
Transmission and negative refractive index (NRI) of metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) metamaterials perforated with different thickness of dielectric layer are studied. It can be found that transmission peaks of rectangular hole are sensitive to the thickness of the dielectric layer. NRI and the bandwidth of NRI are increased with the increasing of the thickness of dielectric layer. NRI of rectangular hole with the thickness of dielectric layer almost follows a linear law when the thickness of dielectric layer in 2–5 μm. A high NRI of metamateriral can be obtained by adjusting the thickness of the dielectric layer of the rectangular hole on MDM metamateriral arrays.
K3Gd(PO4)2:Tb3+ phosphors are synthesized by the solid reaction method, and the phases and luminescence properties of the obtained phosphors are well characterized. The emission spectra of K3Gd(PO4)2:Tb3+ exhibit the typical emissions of Tb3+. Concentration quenching of Tb3+ is not observed in K3Gd(PO4)2:Tb3+, likely because the shortest average distance of Tb3+–Tb3+ in K3Gd(PO4)2:Tb3+ is adequately long such that energy transfer between Tb3+–Tb3+ ions cannot take place effectively. This result indicates that K3Tb(PO4)2 phosphors have potential application in near ultraviolet (n-UV)-convertible phosphors for white light-emitting diodes.
Using the first-principles plane-wave pseudopotential method, based on the density function theory, the electron structure and optical properties of GaAs (100) \beta 2(2 \times 4) and GaAs (100) (4 \times 2) reconstructions are calculated. The formation energy of As-rich \beta 2(2 \times 4) reconstruction is minus and the formation energy of Ga-rich (4 \tiems 2) reconstruction is positive; As-rich \beta 2(2 \times 4) reconstruction is stable and Ga-rich (4 \times 2) reconstruction is unstable. Ga-rich (4 \times 2) reconstruction owns lower work function. The electrons at two reconstructions both move into the bulk and form a band-binding region. Both the absorption and the reflectivity of As-rich 2(2×4) reconstruction are smaller than the Ga-rich (4×2) reconstruction. Asrich \beta 2(2 \times 4) reconstruction is more benefit for the movement of photos through the surface to emit photoelectrons.
In order to couple into or out of a silicon photonic waveguide on silicon on insulator (SOI) substrate from optical fibers, we present a simple but practical method to design a grating coupler. The grating is periodic with fully etched slots; strong reflection between the fully etched grating and the waveguide is avoided by adding an antireflection interface. Theoretical coupling efficiency up to 43% is demonstrated. A taper waveguide used to link the grating and waveguide is also designed.
Based on two-step coordinate transformation along the radial direction, an optical device with three functions is proposed. The proposed device functions as a transparent device, a vision-enabling internal cloak, and a movement-allowing external cloak. The general expressions of material parameters for the optical device are determined, and each function of the device is confirmed using full-wave simulation. The effect of material loss on device performance is also investigated. Future applications for the proposed device include antenna protection and military stealth.
A Yb-doped silica glass fiber laser with a core made by sol-gel method is reported. The maximum power of 1.14 W is obtained with a pump power of 5.46 W at a wavelength of 976 nm. The slope efficiency is 34%. The refractive index fluctuation across the core is below 5×10-4 at a doping level of Yb 0.15 mol%, A2O3 4.0 mol%, and P2O5 2.0 mol%. High background attenuation of 6 dB/m at 1 053 nm limites the slope efficiency and maximum output power.
Sm3+/Yb3+ co-doped tellurite glasses are prepared by melt-quenching technique. The density of the glasses varies between 4.65 and 4.84 g/cm3. The optical absorption spectra consist of eight bands in the wavelength range of 350–2 000 nm, which correspond to the transitions from ground level 6H5/2 to the various excited states of the Sm3+ ion. Energy band gaps vary in the range of 2.73–2.91 eV, and the Urbach energy ranges from 0.21 to 0.27. Emission spectra exhibit four peaks originating from the 4G5/2 energy level centered at 576, 613, 657, and 718 nm. Quenches in emission bands may be due to the energy transfer from the Sm3+ to Yb3+ ions.
YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb phosphors with a triple-doped system are prepared by conventional solid-state reaction method. The fluorescence emission and excitation spectra are measured and analyzed. The influences of Yb3+ doping concentration on the emission of Yb3+ and Nd3+ in YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb are studied. The fluorescence decay spectra, lifetime, and energy transfer efficiency of Ce3+ in different host materials of YAG-Ce and Yb, and YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb are also compared. Furthermore, the trends of fluorescence decay spectra and the lifetimes of Nd3+ and Yb3+ in YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb with the increase of Yb3+concentration are discussed. Results indicate that YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb are good candidates for downconverting phosphor, with energy transfer efficiency reaching as high as 82.8%.
A Dy3+-doped LiYF4 single crystal capable of generating white light by simultaneous blue and yellow light emission of phosphorescent centers is produced. Chromaticity coordinates and photoluminescence intensity vary with excitation wavelength. Under 350, 365, and 388 nm excitation, the crystal shows excellent white light emission. The most efficient wavelength for white light is 388 nm. The CIE coordinates are x=0.316 and y =0.321, and the color temperature (Tc) is 6 368 K. These results indicate that the studied crystal is a potential candidate for ultraviolet light-excited white light-emitting diodes.
We present a theoretical study of surface Tamm states localized at an interface that separates a semi-infinite isotropic left-handed metamaterial (LHM) and one-dimensional photonic crystal made of anisotropic indefinite metamaterial (IMM) (always-cutoff material). We discuss the dispersion properties of the Tamm states in different bandgaps and demonstrate that the cap layer, angular frequency, and arrangement of photonic crystal can provide flexible control for the dispersive properties of the Tamm states.
Silica-based Yb3+-doped glass is prepared by non-chemical vapor deposition. The drawn photonic crystal fiber (PCF) has a strong absorption at 976 nm and emission wavelength of approximately 1 037 nm. The intensity and spectral lineshape of the near infrared (NIR) luminescence of the Yb3+-doped PCF are recorded and discussed in terms of excitation power, excitation wavelength, fiber length, and Yb3+ ion concentration. The emission intensifies as the excitation power and Yb3+ ion concentration increase. The intensity of the shorter wavelength side of the luminescence spectrum decreases as the length of the PCF increases.
The effects of Nd3+ concentration on the visible fluorescence spectroscopic properties of Nd:(Y0.9La0.1)2O3 transparent ceramics are investigated. Under 270 nm excitation, three emission peaks are observed at 396, 426, and 633 nm. When the Nd3+ concentration is increased, intensities of the peaks at 396 and 426 nm increase while the 633 nm peak become weak due to the fluorescence re-absorption effect. Broad luminescence band centered at 426 nm is observed from the fluorescence spectrum stimulated at 358 nm. The emission intensity increases with the increase of Nd3+ ion content firstly, then decreases owing to the concentration quenching of Nd3+ ions.
The self-assembled type-II GaSb quantum dots (QDs) are successfully grown on semi-insulting GaAs (100) matrix by liquid phase epitaxy technique. The topography of QDs with high growth temperature is characterized by atomic force microscopy (AFM). The cap layer, which is needed for the device fabrication, is obtained for only some tens of nanometers. The non-resonant Raman spectra are applied to investigate the GaSb-like optical phonons localized in the QDs and to confirm convincingly the existence of GaSb QDs.
Introducing the finite difference time domain method and perfect match layer absorbing boundary condition, the electro-tunable localized modes in two-dimensional (2D) nematic-liquid-crystal photonic crystal with a point defect (1PD2D-NLCPC) are investigated by numerical simulation. The numerical simulations show that as the direction of the external electrical field varies, the band gap in the 1PD2D-LCPC changes; when the wavelength in the band gap is the wavelength of the sine source wave, the most of optical field energy is localized in the point defect; therefore manipulating the direction of the external electrical field causes the change of the localized mode.
A combination of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and laser-assisted three-dimensional atom probe (3DAP) is employed to study the nanostructure of Dy-doped CeO2, which is a promising ionic conductor. Segregation of Dy atoms at grain boundaries is observed by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) elemental maps. The segregation is checked and confirmed by laser-assisted 3DAP. Moreover, the enrichment of Dy and deficiency of Ce at grain boundaries are quantitatively identified by the 3DAP concentration profile. Data such as these are significant to optimize the electrical conductive property in rare-earth doped Ceria.
Potassium dideuterium phosphate (DKDP) with deuterium content of 60% and potassium dihydrogen phoshate (KDP) crystals are grown by "point-seed" rapid growth method. Optical property including transmittance spectra, conoscopic image, light scattering and laser damage threshold (LDT) are measured. The results show that although the infrared absorption edge of transmission spectra is obviously red-shifted, structure perfection and optical homogeneity of DKDP crystal became poorer. Light scattering have no obvious change. We also find that the value of LDT at 1 053 nm has a 2.5-3.8 \times increase compared with that tested at 526 nm and LDT of Z-cut samples is obviously higher than that of tripler-cut samples.
The optical properties of disperse red 1 (DR1) dye molecules can be changed by controlling the molecular configurations using AlPO4-5 (AFI) and SAPO-47 (CHA) single crystals. Polarized and temperature dependent absorption spectra show that DR1 molecules exist as cis configuration in the cages of CHA crystals. The absorption band for cis-configuration is centered at 432 nm, which does not depend on polarization angle and temperature. However, DR1 molecules are well aligned in the channels of AFI crystal with trans configuration. Its absorption band is centered at 520 nm, which shows strongly anisotropic polarizability and shifts to long wavelength with increasing temperature. It can be used as polarizer and temperature sensor. The second harmonic generation (SHG) and photoluminescence (PL) investigations show that the DR1 trans isomers in AFI matrix have potential applications in nonlinear optics.
By measuring the emission spectra and the fluorescence lifetime of the 4I13=2 state of Er3+ ions in Gd2SiO5 crystal at different temperatures, the effects of temperature on the spectra and the lifetime of the 4I13=2 state are investigated. When the temperature increases, the emission line width for the 4I13=2 -> 4I15=2 transition is broadened, and the main emission lines at 1 596, 1 609, and 1 644 nm shifte toward shorter wavelengths. The measured lifetime of the 4I13=2 state decreases from 13.2 to 8.4 ms with temperature increase from 13 to 300 K, which is mainly due to the temperature dependence of multiphonon relaxation between the 4I13=2 and 4I15=2 states and the changing population distribution among the Stark levels within the 4I13=2 state. The experimental results imply that low temperature condition is better for the ~1.6- \mu m laser output.
The direct replication of W/Si supermirrors is investigated systematically. W/Si supermirrors are fabricated by direct current (DC) magnetron sputtering technology. After deposition, the supermirrors are replicated from the supersmooth mandrels onto ordinary °oat glass substrates by epoxy replication technique. The properties of the supermirrors before and after the replication are characterized by grazing incidence X-ray reflectometry (GIXR) measurement and atomic force microscope (AFM). The results show that before and after replication, the multilayer structures are almost the same and that the surface roughness is 0.240 and 0.217 nm, respectively, which are close to that of the mandrel. It is demonstrated that the W/Si supermirrors are successfully replicated from the mandrel with good performance.
The omni-directional reflection characteristics of one-dimensional photonic crystals composed of Ta2O5/MgF2 multi-quantum well (MQW) are studied using the transfer matrix method. An omni-directional reflector consisting of three and four Ta2O5/MgF2 MQWs is investigated. Results show that the photonic band gap of the photonic crystal composed of three and four Ta2O5/MgF2 MQWs, which are within the wavelength ranges of 402–712 and 412–1,023 nm, respectively, could cover the entire visible region. The relationship among the width of the band gap, its location, reflectivity rate, and incident angle of the incident light is analyzed. The optimal structural parameters of the MQW of the omni-directional reflector in the visible region are also calculated. The calculations provide a guide for the design of omni-directional reflection devices in the visible region.
In this letter, Eu2+-activated MO-B2O3 (M=Ca, Sr, and Ba) glasses are prepared in reductive atmosphere and their long lasting phosphorescence properties are studied. The intensity of the phosphorescence for the glasses is Sr>Ca>Ba. The light-induced electron paramagnetic resonance signal is observed after the irradiation of an ultraviolet lamp, which is due to the electron trapped by oxygen vacancy. The energy depth of the glasses is calculated using Hoogenstraaten's method.
Bi-doped SiO2–Al2O3–GeO2 fiber preforms are prepared by modified chemical vapor deposition (MCVD) and solution doping process. The characteristic spectra of the preforms and fibers are experimentally investigated, and a distinct difference in emission between the two is observed. Under 808-nm excitation, an ultra-broad near-infrared (NIR) emission with full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of 495 nm is observed in the Bi-doped fiber. This observation, to our knowledge, is the first in this field. The NIR emission consists of two bands, which may be ascribed to the Bi0 and Bi+ species, respectively. This Bi-doped fiber is promising for broadband optical amplification and widely tunable laser.
Pure zinc blende structure GaAs/AlGaAs axial heterostructure nanowires (NWs) are grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition on GaAs(111) B substrates using Au-catalyzed vapor-liquid-solid mechanism. Al adatom enhances the influence of diameters on NWs growth rate. NWs are grown mainly through the contributions from the direct impingement of the precursors onto the alloy droplets and not so much from adatom diffusion. The results indicate that the droplet acts as a catalyst rather than an adatom collector.
Different up-conversion luminescent spectra of Er^(3+) ions were observed in the oxyfluoride glass-ceramics. The ratio of two fluorides in the original compositions was modified in order to form different nanocrystals. The intensity of up-conversion luminescence increased sharply when the ratio of PbF2 and CdF2 was 40:10. The data of differential thermal analysis and X-ray diffraction were used to explain the optimization fluoride ratio. The intensity of up-conversion luminescence is not only decided by the crystallizability but also mainly related with the stoichiometric proportion of fluoride nanocrystals in the glass-ceramics.